# BITSCTF2025 Write Up
# Cryptography
# The most wanted lagomorph
给了一串密文
簾簿 簾簽 簽籶 簽籀 簿簼 簼簻 簾簻 簽籁 簾簿 簿米 籀簽 簾籂 簽米 簾簼 籀簽 簽籴 簾籂 簼簻 簿籵 籀籂 簾簽 簽簿 簽簿 簼簻 簾簾 簽簿 簾簻 簼簾 簽米 簽簽 簾籶 簿籲 簾籂 簾簽 簾籂 簼簻 簿簼 簾簾 簼簺 簾簾 簾簻 簽籀 簿簽 籀簿 簾簽 簼簻 簿籴 籀籀 簽籲 簿籴 簽籲 簼簽 簾簼 簽簽 簽簿 簼簹 簽籲 簼簹 簾簿 籀籂 簾籶 簾簾 簿籴 籀簽 簿簾 簽簿 簿簽 簽簽 簾簾 簽簽 簽籲 簾簼 簾籂 簾籁 簽籶 簾簾 簿簾 簾簿 簽籶 簾簾 簾簿 簾簽 簽籶 籀簻 簽米 簼簹 簼簾 籀籂 簾籶 簽簽 簾簻 簼簻 簾簺 簼簻 簿籁 簼簿 簾籂 簼簺 簿籁 簾籶 簾簼 簼簼 簽簿 簾簺 簾籀 簿籴 簽籲 簼簾 簿簻 簽簽 簽籲 簾簾 |
这里可以想到 ROT8000 加密,首先做一遍 ROT8000
56 54 4m 47 63 32 52 48 56 6j 74 59 4j 53 74 4k 59 32 6l 79 54 46 46 32 55 46 52 35 4j 44 5m 6i 59 54 59 32 63 55 31 55 52 47 64 76 54 32 6k 77 4i 6k 4i 34 53 44 46 30 4i 30 56 79 5m 55 6k 74 65 46 64 44 55 44 4i 53 59 58 4m 55 65 56 4m 55 56 54 4m 72 4j 30 35 79 5m 44 52 32 51 32 68 36 59 31 68 5m 53 33 46 51 57 6k 4i 35 62 44 4i 55 |
发现它很像 Hex, 但是 abcdef 变成了 ijklm
先做一次 ROT13
56 54 4z 47 63 32 52 48 56 6w 74 59 4w 53 74 4x 59 32 6y 79 54 46 46 32 55 46 52 35 4w 44 5z 6v 59 54 59 32 63 55 31 55 52 47 64 76 54 32 6x 77 4v 6x 4v 34 53 44 46 30 4v 30 56 79 5z 55 6x 74 65 46 64 44 55 44 4v 53 59 58 4z 55 65 56 4z 55 56 54 4z 72 4w 30 35 79 5z 44 52 32 51 32 68 36 59 31 68 5z 53 33 46 51 57 6x 4v 35 62 44 4v 55 |
发现变成了 vwxyz, 可以用 Atbash Cipher 就变回 abcde 了
56 54 4a 47 63 32 52 48 56 6d 74 59 4d 53 74 4c 59 32 6b 79 54 46 46 32 55 46 52 35 4d 44 5a 6e 59 54 59 32 63 55 31 55 52 47 64 76 54 32 6c 77 4e 6c 4e 34 53 44 46 30 4e 30 56 79 5a 55 6c 74 65 46 64 44 55 44 4e 53 59 58 4a 55 65 56 4a 55 56 54 4a 72 4d 30 35 79 5a 44 52 32 51 32 68 36 59 31 68 5a 53 33 46 51 57 6c 4e 35 62 44 4e 55 |
然后把 hex 转成字符
VTJGc2RHVmtYMStLY2kyTFF2UFR5MDZnYTY2cU1URGdvT2lwNlN4SDF0N0VyZUlteFdDUDNSYXJUeVJUVTJrM05yZDR2Q2h6Y1hZS3FQWlN5bDNU |
看看 base64
U2FsdGVkX1+Kci2LQvPTy06ga66qMTDgoOip6SxH1t7EreImxWCP3RarTyRTU2k3Nrd4vChzcXYKqPZSyl3T |
然后标题是 The most wanted lagomorph, google 搜索 "The most wanted lagomorph" 后是 dennis 的兔子
有一个 Cipher 叫 Rabbit Cipher , 把 dennis 作为密码可以用 CapfEncoder 解密
BITSCTF{f3rb_1_kn0w_wh47_w3_4r3_60nn4_d0_70d4y} |
# Alice n bob in wonderland
一道 ECDSA 的题。首先 Alice 和 Bob 会互发消息,每条消息有密文和签名。
然后使用 IV 作为 random 的种子,使用 ECDSA 进行签名。
aes_key = shared_secret[:16] | |
iv = shared_secret[16:] | |
random.seed(int(iv.hex(),16)) |
然后我们是作为 ManInTheMiddle 的位置,可以转发 Alice 的消息给 Bob, 也可以伪造消息给 Bob. 但是注意它们会验证签名,并且在验证的时候给出 Ciphertext 的解密,并且如果失败二次就停止了。也就是有一次解密 Oracle 的机会。
首先我们可以拿到 IV 的值,通过构造 然后异或 就可以得到 IV.
另一个弱点
def sign(message, private_key:SigningKey): | |
message = message.encode() | |
k = random.randint(1, SECP256k1.order - 1) | |
signature = private_key.sign(message,hashfunc=hashlib.sha256 ,k=k) | |
return signature |
在签名 message 的时候,密钥是用 random 生成的,也就是如果我们拿到了种子,就可以掌握签名密钥.
然后通过
def compute_shared_secret(private_key, public_key): | |
shared_point = private_key.privkey.secret_multiplier * public_key.pubkey.point | |
shared_secret_bytes = shared_point.to_bytes() | |
return hashlib.sha256(shared_secret_bytes).digest() | |
shared_secret = compute_shared_secret(alice_private_key, bob_public_key) |
这是计算 shared_secret 的方式,而 AES 密钥包含在 shared_secret 里面
所以思路就是:
- 先拿到 IV
- 然后就有 k, 也就是
private_key - 然后可以知道
shard_secret,知道 AES 的密钥
最后给 Alice 发送消息
print(f"\nSend to Aice:") | |
ciphertext_forged = bytes.fromhex(input("Ciphertext (hex): ")) | |
signature_forged = bytes.fromhex(input("Signature (hex): ")) | |
plaintext = decrypt(ciphertext_forged) | |
print("Debug: ",plaintext) | |
verified = verify(plaintext,signature_forged,bob_public_key) | |
if verified and plaintext.decode() == "Can I have the key again, I think I forgot where I kept the key.": | |
print("Very good, now we wait.") | |
ciphertext = encrypt(secret) | |
signature = sign(secret,alice_private_key) | |
print(f"\nIntercepted from Alice:\nCiphertext: {ciphertext.hex()}\nSignature: {signature.hex()}\n") |
这里的 secret 就是 flag 了
完整代码:
from pwn import * | |
import re | |
from binascii import hexlify, unhexlify | |
from hashlib import sha256 | |
import random | |
from ecdsa import SigningKey, SECP256k1, VerifyingKey | |
from Crypto.Cipher import AES | |
from Crypto.Util.Padding import pad, unpad | |
def xor(a,b): | |
return bytearray([x^y for (x,y) in zip(a,b)]) | |
io = process(["py","chall.py"]) | |
msg = io.recvuntil(b"Ciphertext (hex): ").decode() | |
print(msg) | |
alice_public_key_hexstr = re.search(r"Alice's public key:\s*([0-9a-fA-F]+)", msg).group(1) | |
bos_public_key_hexstr = re.search(r"Bob's public key:\s*([0-9a-fA-F]+)", msg).group(1) | |
alice_public_key = VerifyingKey.from_string(unhexlify(alice_public_key_hexstr), curve=SECP256k1) | |
bob_public_key = VerifyingKey.from_string(unhexlify(bos_public_key_hexstr), curve=SECP256k1) | |
alice_ciphertext_1 = re.search(r"Ciphertext:\s*([0-9a-fA-F]+)", msg).group(1) | |
alice_signature_1 = re.search(r"Signature:\s*([0-9a-fA-F]+)", msg).group(1) | |
c1 = b"1"*16 + b"\x00"*16 + b"1"*16 | |
c1_hex = hexlify(c1) | |
io.sendline(c1_hex) | |
print(io.recvuntil(b"Signature (hex): ").decode()) | |
io.sendline(c1_hex) | |
msg = io.recvuntil(b"Ciphertext (hex): ").decode() | |
print(msg) | |
pt_hexstr = re.search(r"and this is what they found:\s*([0-9a-fA-F]+)", msg).group(1) | |
pt_bytes = unhexlify(pt_hexstr) | |
iv_bytes = xor(pt_bytes[:16], pt_bytes[32:48]) | |
print(iv_bytes) | |
random.seed(int(iv_bytes.hex(),16)) | |
# k = random.randint(1, SECP256k1.order - 1) | |
def sign(message, private_key:SigningKey, k): | |
signature = private_key.sign(message,hashfunc=hashlib.sha256 ,k=k) | |
return signature | |
io.sendline(alice_ciphertext_1.encode()) | |
io.sendlineafter(b"Signature (hex): ", alice_signature_1.encode()) | |
# io.sendline(c1_hex) | |
# print(io.recvuntil(b"Signature (hex): ").decode()) | |
k = random.randint(1, SECP256k1.order - 1) | |
k = random.randint(1, SECP256k1.order - 1) | |
# io.sendline(hexlify(sig_c1)) | |
io.recvuntil(b"Ciphertext: ") | |
ciphertext = bytes.fromhex(io.readline().decode()) | |
io.recvuntil(b"Signature: ") | |
signature = bytes.fromhex(io.readline().decode()) | |
bob_sigature = signature | |
print("BEFORE") | |
def compute_shared_secret(private_key, public_key): | |
shared_point = private_key.privkey.secret_multiplier * public_key.pubkey.point | |
shared_secret_bytes = shared_point.to_bytes() | |
return hashlib.sha256(shared_secret_bytes).digest() | |
r = int.from_bytes(signature[:32]) | |
s = int.from_bytes(signature[32:]) | |
z = int.from_bytes(sha256(b"msg2").digest()) % SECP256k1.order | |
print(r,s) | |
io.sendlineafter(b"Ciphertext (hex): ", ciphertext.hex().encode()) | |
io.sendlineafter(b"Signature (hex): ", signature.hex().encode()) | |
maybe_d = (((s * k) - z) * pow(r, -1, SECP256k1.order)) % SECP256k1.order | |
bob_private_key = SigningKey.from_secret_exponent(maybe_d, curve=SECP256k1) | |
shared_secret = compute_shared_secret(bob_private_key, alice_public_key) | |
assert(shared_secret[16:] == iv_bytes) | |
aes_key = shared_secret[:16] | |
# print(io.recv(512).decode()) | |
print(io.recvuntil(b"Send to Aice:").decode()) | |
chosen_plaintext = b"Can I have the key again, I think I forgot where I kept the key." | |
cipher = AES.new(aes_key, AES.MODE_CBC, iv_bytes) | |
ciphertext = cipher.encrypt(pad(chosen_plaintext, AES.block_size)) | |
k = random.randint(1, SECP256k1.order - 1) | |
signature = bob_private_key.sign(chosen_plaintext,hashfunc=sha256 ,k=k) | |
io.sendlineafter(b"Ciphertext (hex): ", ciphertext.hex().encode()) | |
io.sendlineafter(b"Signature (hex): ", signature.hex().encode()) | |
# then alice should send us the flag encrypted... | |
# ... along with a signature that we can ignore | |
# print(io.recv(512).decode()) | |
io.readuntil(b"Ciphertext: ") | |
flag_ciphertext = bytes.fromhex(io.readline().decode()) | |
io.readuntil(b"Signature: ") | |
flag_signature = bytes.fromhex(io.readline().decode()) | |
cipher = AES.new(aes_key, AES.MODE_CBC, iv_bytes) | |
plaintext = unpad(cipher.decrypt(flag_ciphertext), AES.block_size) | |
# flag = plaintext[59:].decode() | |
print(plaintext.decode()) | |
# n = SECP256k1.order | |
# s = pow(k,-1,n) * (z + r*d) |
# Noob RSA returns
在 RSA 加密完后,额外给了一个
第一个思路是质因数分解,但是不太可能,因为质因数很大。
通过同于方程求解也不行,因为 是高次方的
但是 RSA 有个结论
它可以写成
这里 是关于 的逆,通常很大 所以 , 测试下来, 的值在 直接可以枚举
然后 Python 代码
from sympy import Eq, symbols, solve | |
from tqdm import tqdm | |
from Crypto.Util.number import long_to_bytes | |
e = 65537 | |
n = 94391578028846794543970306963076155289398888845132329034244336898352288130614402434536624297683695128972774452047972797577299176726976054101512298009248486464357336027594075427866979990479026404794249095503495046303993475122649145761379383861274918580282133794104162177538259963029805672413580517485119968223 | |
ct = 39104570513649572073989733086496155533723794051858605899505397827989625611665929344072330992965609070817627613891751881019486310635360263164859429539044097039969287153948226763672953863052936937079161030077852648023719781006057880499973169570114083902285555659303311508836688226455433255342509705736365222119 | |
K = 20846957286553798859449981607534380028938425515469447720112802165918184044375264023823946177012518880630631981155207307372567493851397122661053548491580627249805353321445391571601385814438186661146844697737274273249806871709168307518276727937806212329164651501381607714573451433576078813716191884613278097774416977870414769368668977000867137595804897175325233583378535207450965916514442776136840826269286229146556626874736082105623962789881101475873449157946816513513532838149452759771630220014344325387486921028690085783785067988074331005737389865053848981113695310344572311901555735038842261745556925398852334383830822697851 | |
C = 0xbaaaaaad | |
D = 0xdeadbeef | |
A= 0xbaadf00d | |
p = symbols("p",integer=True) | |
START=42675 | |
# START=1 | |
flag = False | |
for z in tqdm(range(START,e+1)): | |
equation = Eq(K*e, (A*p**2 - C*p + D)*(1+z*(n/p-1)*(p-1))) | |
solutions = solve(equation, p) | |
for sol in solutions: | |
if sol.is_integer: | |
print(sol) | |
flag = True | |
break | |
if flag: | |
break | |
# p = 10406216443192169173533723167461845081683996237790486467542778667477564930803546070928131853072839096935544813786122096301171127932695303325352097678393621 | |
phi = (n//p-1)*(p-1) | |
d = pow(e, -1, phi) | |
m = pow(ct, d, n) | |
print(long_to_bytes(m).decode()) |
# RSA Bummer
TODO: 没看懂
https://github.com/IC3lemon/CTF-reports/tree/main/BITSCTF-2025/crypto/RSA Bummer
solution:
#!/usr/bin/env python3 | |
from pwn import remote, context, log | |
from math import gcd | |
from Cryptodome.Util.number import long_to_bytes, inverse | |
from gmpy2 import iroot | |
context.log_level = "debug" | |
def rsa_decrypt_modp(c, e, p): | |
g = gcd(e, p - 1) | |
if g == 1: | |
d = inverse(e, p - 1) | |
return pow(c, d, p) | |
else: | |
e_prime = e // g | |
t = (p - 1) // g | |
d_prime = inverse(e_prime, t) | |
X = pow(c, d_prime, p) | |
log.info("Computed X = m^g mod p: {}".format(X)) | |
root, exact = iroot(X, g) | |
if exact: | |
log.info("Successfully extracted integer g-th root using gmpy2") | |
return int(root) | |
else: | |
raise Exception("No valid g-th root found") | |
def recv_until_keyword(r, keyword): | |
while True: | |
line = r.recvline().decode().strip() | |
log.debug("Received: " + line) | |
if keyword in line: | |
return line | |
def get_lucky_output(r, x): | |
r.recvuntil("Enter your lucky number : ") | |
r.sendline(str(x)) | |
line = r.recvline().decode().strip() | |
if "Your lucky output" not in line: | |
line = r.recvline().decode().strip() | |
val = int(line.split(':')[-1].strip()) | |
r.recvline() | |
return val | |
def main(): | |
HOST = "chals.bitskrieg.in" | |
PORT = 7001 | |
r = remote(HOST, PORT) | |
line = recv_until_keyword(r, "Pseudo_n") | |
pseudo_n = int(line.split('=')[-1].strip()) | |
log.info("Parsed Pseudo_n = {}".format(pseudo_n)) | |
line = recv_until_keyword(r, "e =") | |
e = int(line.split('=')[-1].strip()) | |
log.info("Parsed e = {}".format(e)) | |
cts = [] | |
for i in range(3): | |
line = recv_until_keyword(r, "Ciphertext") | |
ct = int(line.split('=')[-1].strip()) | |
cts.append(ct) | |
log.info("Parsed Ciphertext {}: {}".format(i+1, ct)) | |
F3 = get_lucky_output(r, 3) | |
log.info("F(3) = {}".format(F3)) | |
F4 = get_lucky_output(r, 4) | |
log.info("F(4) = {}".format(F4)) | |
n_val = F3 + 4 * F4 | |
log.info("Recovered n (p * r) = {}".format(n_val)) | |
r_val = gcd(n_val, pseudo_n) | |
log.info("Recovered r = {}".format(r_val)) | |
p_val = n_val // r_val | |
log.info("Recovered p = {}".format(p_val)) | |
flag_parts = [] | |
for idx, ct in enumerate(cts, start=1): | |
m_int = rsa_decrypt_modp(ct, e, p_val) | |
part = long_to_bytes(m_int) | |
log.info("Decrypted part {}: {}".format(idx, part)) | |
flag_parts.append(part) | |
flag = b"".join(flag_parts) | |
log.success("Flag: {}".format(flag.decode())) | |
r.close() | |
if __name__ == "__main__": | |
main() | |
#F(x) is the output of the func 'lmao' you can get that F(x)+(x+1)F(x+1)=p*r. send 2 small values to the server and use the printed value which is psudo_n=(r*(e^p mod q)) then gcd(psudo_n,n) you can get r then p=n/r decrypt mod p will give the flag |
# Leaky Game
TODO
https://github.com/E-HAX/writeups/tree/main/2025/bitsctf/osint/leaky_game
# Reverse Engineering
# Praise Our RNG Gods
Given is a Python Byte Code
```0 LOAD_CONST 0 (0)
2 LOAD_CONST 1 (None)
4 IMPORT_NAME 0 (random)
6 STORE_NAME 0 (random)
...
14 LOAD_CONST 3 (322420958)
16 BINARY_OP 12 (^)
18 BINARY_OP 5 ()
20 LOAD_CONST 4 (2969596945L)
22 BINARY_OP 5 ()
24 STORE_FAST 1 (password)
26 LOAD_FAST 1 (password)
28 RETURN_VALUE```
BINARY_OP 5 () 这里应该是乘法,用过验证回复的数字得到
Using a website https://www.codeconvert.ai/assembly-to-python-converter
,we can decode it to python code.
import random | |
import os | |
seed = int.from_bytes(os.urandom(8), "big") | |
random.seed(seed) | |
flag = "REDACTED" | |
def generate_password(): | |
global i | |
password = (random.getrandbits(32) ^ i ^ 195894762) ^ 322420958 | |
return password | |
print("Vault is locked! Enter the password to unlock.") | |
i = 1 | |
while True: | |
password = generate_password() | |
attempt = input("> ") | |
if not attempt.isdigit(): | |
print("Invalid input! Enter a number.") | |
continue | |
difference = abs(password - int(attempt)) | |
if difference == 0: | |
print("Access Granted! Here is your flag:") | |
print(flag) | |
break | |
print(f"Access Denied! You are {difference} away from the correct password. Try again!") | |
i += 1 |
The problem is, the password shoud be a 32bit integer,however when we connnect to the nc chals.bitskrieg.in 7007 , it replies a 64 bit integer.
UPD: Found it, the result was wrong. The actual generate password should be
def generate_password(): | |
global i | |
password = random.getrandbits(32) * ( i ^ 195894762 ^ 322420958) * 2969596945 | |
return password |
The solution should be that the random library of python
uses Mersenne Twister Algorithm, which is not secure.
If we know some consecutive random numebrs generated,
we can predict the next one.
Reference: (In Chinese) https://liam.page/2018/01/12/Mersenne-twister/
还有另一个方便的方法,使用 mt19937predictor 这个 python 包
先 pip 安装
pip install mersenne-twister-predictor |
使用:
import random | |
from mt19937predictor import MT19937Predictor | |
predictor = MT19937Predictor() | |
for _ in range(624): | |
x = random.getrandbits(32) | |
predictor.setrandbits(x, 32) # Submit samples here | |
# When enough samples are given, you can start predicting: | |
assert random.getrandbits(32) == predictor.getrandbits(32) |
# Reverse Mishap
用 IDA 打开,查找 String
.rodata:0000000000094013 00000050 C /rustc/051478957371ee0084a7c0913941d2a8c4757bb9/library/core/src/char/methods.rs |
可以发现这是 Rust 的程序, 051478957371ee0084a7c0913941d2a8c4757bb9 这个
去 rust 的 github 里搜索这个,在 pull request 里发现是 1.80.0 Release 版本
然后看依赖项
发现依赖 generic-array 之类的依赖,建立 Cargo.toml 里面写
[package] | |
name = "demo" | |
version = "0.1.0" | |
edition = "2021" | |
[dependencies] | |
rand_core = "0.6.4" | |
rand_chacha = "0.3.1" | |
generic-array = "0.14.7" | |
cipher = "0.4.4" | |
aes = "0.8.4" | |
ppv-lite86 = "0.2.20" | |
rand = "0.8" |
这里要用一个 IDA 插件叫 capa
pip install capa | |
pip install pip install flare-capa | |
pip install pyqt5 |
然后把 capa/ida/plugin/capa_explorer.py 拷贝到 IDA 的 plugin 文件夹下。就可以在 IDA 里用 Edit, Plugin 里打开了
https://blog.diefunction.io/ctf/bitsctf-reverse-mishap
发现运行不了,我然后换一种方式:先下载 capa 的 windows Release,拷贝到要分析的文件的同文件夹下
然后运行 cmd,首先 clone rules
git clone https://github.com/mandiant/capa-rules.git |
然后运行
capa -r capa-rules/ <my_rust_binary> |
之前插件运行不了的原因是,这个 capa 有 BUG!! 在 IDA 9.0 的时候 bin_search 被替换成了 bin_search3 所以报错了。首先进入
C:\Users\<username>\AppData\Local\Programs\Python\Python313\Lib\site-packages\capa\features\extractors\ida |
里面找到 helpers.py 把里面的 bin_search 替换成 bin_search3 就可以了
然后安装 Rust 依赖,首先去 Rust 官网下载 https://www.rust-lang.org/learn/get-started
使用 rustc --version 可以验证安装
使用下面的生成一个 demo
cargo new demo | |
cd demo |
然后进去修改配置文件
[package] | |
name = "demo" | |
version = "0.1.0" | |
edition = "2021" | |
[dependencies] | |
rand_core = "0.6.4" | |
rand_chacha = "0.3.1" | |
generic-array = "0.14.7" | |
cipher = "0.4.4" | |
aes = "0.8.4" | |
ppv-lite86 = "0.2.20" | |
rand = "0.8" |
我发现需要用 ubuntu 来写 rust,因为到手的不是 windows 的文件
去 ubuntu 安装 rust
curl --proto '=https' --tlsv1.2 -sSf https://sh.rustup.rs | sh |
安装完可以 source $HOME/.cargo/env 一下
把这个编译出来后,用 IDA 生成 SIG 签名,然后在 Load 到我们要分析的程序,会发现有一些函数就可以被识别出来了。
但是大部分还没被识别出来。之后再看。这个太难了。
# Appreciation of Art
用 GDB 调试一下,可以装 pwngdb 这个插件
使用 b *0x401001 可以在某个地址下断点
也用 IDA 试了一下,发现根本没办法调试,只有一个 start 函数,而且很大,IDA 无法反编译
先用 GDB 打开,在运行时候 dump meory,具体操作
gdb a.art |
然后输入 r 然程序跑起来等待输入。然后 control+C 打断程序,然后 dump memory
vmmap |
输出
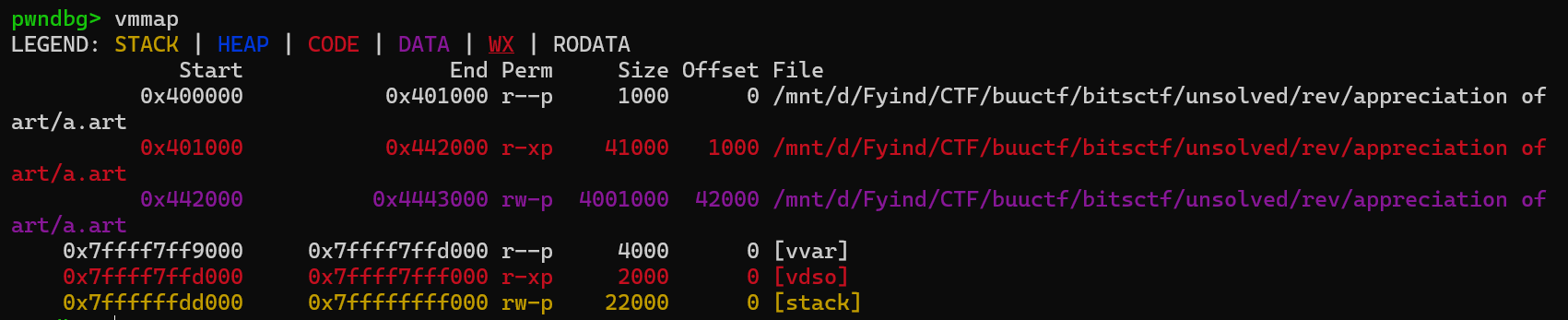
把 Code 的那一段 dump 下来 0x442000 - 0x4443000
dump memory pie.dmp 0x442000 0x4443000 |
然后退出,cat 这个 memory (VSCODE 里的 hex editor 打开,然后搜索也行)
@���F��I��H���@�@�@no memory! | |
␦123456789:;<=>?@abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz[\]^_`abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz{|}~������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������ in : unknown format! | |
���What is the name of the character hiding in this binary (lowercase with underscores if needed): gg here's your flag %s | |
Are you hallucinating? | |
�J��E��`�J��"���J��#���`What is the name of the character hiding in this binary (lowercase with underscores if needed): ���N��VA���o���dBITSCTF{1_l0v3_0bfu5c4t1ng_thi1ng5_r4nd0mly_0e54826a}*?((#.2?*6;.#*/).shstrtab.text.data |
在里面发现了 flag.
# Hardware
# oldSkool
这个题关于 Radio Signal Processing, 这里给了一个 iq 文件 TODO:没看懂
import numpy as np | |
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt | |
from scipy.signal import hilbert | |
from scipy.io import wavfile | |
# 1. Wczytanie pliku IQ | |
file_path = "modulated.iq" | |
iq_data = np.fromfile(file_path, dtype=np.complex64) | |
# 2. Parametry | |
Fs = 24000 # Sampling rate 24kHz | |
Fc = 1550000 # Przybliżona nośna (np. 1550 kHz) | |
t = np.arange(len(iq_data)) / Fs | |
# 3. Przemiana częstotliwości (mixing) | |
demod_signal = iq_data * np.exp(-1j * 2 * np.pi * Fc * t) | |
# 4. Demodulacja AM (obwiednia) | |
audio_signal = np.abs(hilbert(demod_signal.real)) | |
# 5. Normalizacja i zapis do pliku WAV | |
audio_signal = (audio_signal / np.max(np.abs(audio_signal)) * 32767).astype(np.int16) | |
wavfile.write("output.wav", Fs, audio_signal) | |
print("Demodulacja zakończona! Otwórz output.wav, aby odsłuchać.") |
# %lution
首先这是一个 signal 文件,我们用 Universal Radio Hacker 打开这个文件,可以得到二进制码,在 Cyberchef 里用 from binary 拿到 flag
# MISC
# Ghost Protocol
TODO
https://github.com/V1rg1lee/writeups/tree/main/2025-BITSkrieg/ghosting-protocol
# Seed fund
TODO
https://github.com/V1rg1lee/writeups/tree/main/2025-BITSkrieg/seed-fund
# DFIR
# virus camp
TODO
https://odintheprotector.github.io/2025/02/09/bitsctf2025-dfir.html
# 其他 Writeups 链接
https://github.com/Vatsallavari/BITSCTF/tree/main
https://mindcrafters.xyz/writeups/hardware-bitskrieg/
https://zwique.gitbook.io/zwique_notes/writeups/random-ctf-writeup/noob-rsa-returns
https://mindcrafters.xyz/writeups/rev-bitskrieg/#appreciation-of-art